Round up or ceil in sas using ceil function.
Sas function floor ceil.
It will be easier to understand their role now that you understood the explanation above about sas round function.
The ceiling function is usually denoted by ceil x or less commonly ceiling x in non apl computer languages that have a notation for this function.
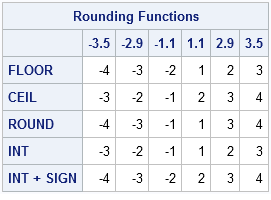
The ceil function rounds up.
Unlike the floorz function the floor function fuzzes the result.
The ceilz function does not fuzz the result.
For ceiling and.
In the case below it will return 2.
The ceilz function does not fuzz the result.
Round off the column in sas is accomplished by round function.
The floorz function uses zero fuzzing.
The j programming language a follow on to apl that is designed to use standard keyboard symbols uses.
The round function rounds to the nearest integer.
Let s see an example of each.
Unlike the ceilz function the ceil function fuzzes the result.
The floor function rounds down.
If the argument is within 1e 12 of an integer the floor function fuzzes the result to be equal to that integer.
Therefore with the floorz function you might get unexpected results.
If the argument is within 1e 12 of an integer the ceil function fuzzes the result to be equal to that integer.
The floor function fuzzes the results so that if the results are within 1e 12 of an integer the floor function returns that integer.
Unlike the ceilz function the ceil function fuzzes the result.
The ceilz function does not fuzz the result.
Sas does not have a built in function that rounds away from zero but you can combine the sign function with another function to round away from zero.
Therefore with the ceilz function you might get unexpected results.
Utility of sas floor and sas ceil functions.
Therefore with the ceilz function you might get unexpected results.
Briefly i want to mention the sas floor and sas ceil functions.
Unlike the ceilz function the ceil function fuzzes the result.
The floor function returns the largest integer that is less or equal to the argument.
Therefore with the ceilz function you might get unexpected results.
Therefore with the floorz function you might get unexpected results.
If the argument is within 1e 12 of an integer the ceil function fuzzes the result to be equal to that integer.
The floorz function does not fuzz the result.
If the argument is within 1e 12 of an integer the ceil function fuzzes the result to be equal to that integer.